Difference between revisions of "VPN"
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 73: | Line 73: | ||
{{go to top}} | {{go to top}} | ||
The following config is best done from the terminal on a MikroTik device. | The following config is best done from the terminal on a MikroTik device. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Note: You can use the following config to connect two MikroTik systems. Just replicate the config below on each system you wish to connect.'' | ||
/ip ipsec policy | /ip ipsec policy | ||
| Line 233: | Line 235: | ||
==Persistent SSH Tunnels== | ==Persistent SSH Tunnels== | ||
| − | |||
The following is how to create a persistent SSH Tunnel between two systems. This is handy if you want to secure data flowing across networks, or even setup a tunnel without messing with VPN configuration. | The following is how to create a persistent SSH Tunnel between two systems. This is handy if you want to secure data flowing across networks, or even setup a tunnel without messing with VPN configuration. | ||
| Line 245: | Line 246: | ||
Now switch to the user and generate an SSH key: | Now switch to the user and generate an SSH key: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| − | su -s /bin/bash | + | su -s /bin/bash autossh |
cd ~ | cd ~ | ||
ssh-keygen -b 4096 | ssh-keygen -b 4096 | ||
| Line 257: | Line 258: | ||
===Copy public key to target system=== | ===Copy public key to target system=== | ||
| − | You will need to copy '''''id_rsa.pub''''' file from '''''/home/ | + | You will need to copy '''''id_rsa.pub''''' file from '''''/home/autossh/.ssh/''''' to the '''''authorized_keys''''' file on the remote system you want to connect to for the tunnel. |
''Note: It is recommended that you also create a normal user on the remote system and not use root.'' | ''Note: It is recommended that you also create a normal user on the remote system and not use root.'' | ||
| Line 268: | Line 269: | ||
===Setup script=== | ===Setup script=== | ||
| − | Copy the following script, making the necessary changes as specified between the <> and place on the system that will initiate the tunnel ( | + | Copy the following script, making the necessary changes as specified between the <> and place on the system that will initiate the tunnel (here we will save it as /opt/ssh-tunnel.sh): |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
#!/bin/sh | #!/bin/sh | ||
# | # | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
su -s /bin/sh autossh -c 'autossh -M 0 -N -o "ServerAliveInterval 30" -o "ServerAliveCountMax 3" -o "ExitOnForwardFailure=yes" -f -T -R localhost:<target port>:<local IP or localhost>:<local port> <user>@<domain>' | su -s /bin/sh autossh -c 'autossh -M 0 -N -o "ServerAliveInterval 30" -o "ServerAliveCountMax 3" -o "ExitOnForwardFailure=yes" -f -T -R localhost:<target port>:<local IP or localhost>:<local port> <user>@<domain>' | ||
| − | </pre> | + | </pre> |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 307: | Line 306: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| − | chmod +x | + | chmod +x /opt/ssh-tunnel.sh |
</pre> | </pre> | ||
===Tunnel at startup=== | ===Tunnel at startup=== | ||
| − | To have | + | To have the tunnel up when the system restarts, choose one of the following methods |
| + | |||
| + | ====rc.local==== | ||
| + | Add a line to /etc/rc.local that calls the script. | ||
| + | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| − | /opt/ | + | # Start AutoSSH tunnel at boot |
| + | /opt/ssh-tunnel.sh | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
''Note: You may have to enable rc.local on Ubuntu and Debian based systems via systemd. Refer to your distributions documentation for information on how to enable it.'' | ''Note: You may have to enable rc.local on Ubuntu and Debian based systems via systemd. Refer to your distributions documentation for information on how to enable it.'' | ||
| + | ====systemd==== | ||
| + | To have the script start at boot with systemd, create the following file and add it to /etc/systemd/system/ssh-tunnel.service | ||
| + | |||
| + | =====ssh-tunnel.service===== | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | [Unit] | ||
| + | Description=AutoSSH Tunnel at boot | ||
| + | |||
| + | [Service] | ||
| + | Type=oneshot | ||
| + | ExecStart=/opt/ssh-tunnel.sh | ||
| + | |||
| + | [Install] | ||
| + | WantedBy=multi-user.target | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =====Enable service===== | ||
| + | To enable the service to run via systemd run: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | systemctl enable ssh-tunnel.service | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
== GRE Tunnel == | == GRE Tunnel == | ||
Latest revision as of 01:16, 23 February 2024
 VPN Security |
The following contains information on how to setup a Virtual Private Network (VPN) connection using various popular software packages and hardware devices.
IPSEC
Information on how to setup IPSEC tunnels.
strongSwan to strongSwan
Use the following config for a strongSwan[1] to strongSwan configuration. Make sure the left and right IP addresses are updated to match each system. You can use the same ipsec.secrets file on both systems without changing the IP address order, although I recommend changing it to having the local IP on the left and the remote on the right as shown below.
ipsec.conf
/sec/ipsec/conf:
conn <name>
authby=secret
auto=route # can also be start
keyexchange=ike
left=<your local IP>
right=<remote IP of Mikrotik system>
leftikeport=500
rightikeport=500
type=transport
esp=aes128gcm16!
dpddelay=5
dpdtimeout=20
dpdaction=clear # can also be restart
ipsec.secrets
/etc/ipsec.secrets:
<your local IP> <remote IP of Mikrotik system> : PSK "<Put your preshared key here>"
strongSwan to MikroTik
Use the following configurations to connect a system running strongSwan to a MikroTik[2] device using IPSEC.
strongSwan config
The following configuration will work on FreeBSD or Linux systems with strongSwan installed.
ipsec.conf
/etc/ipsec.conf:
conn <name>
authby=secret
auto=route
keyexchange=ike
left=<your local IP>
right=<remote IP of Mikrotik system>
leftikeport=500
rightikeport=500
type=transport
ike=aes256-sha1-modp1024!
esp=aes256-sha1!
dpddelay=5
dpdtimeout=20
dpdaction=clear
ipsec.secrets
/etc/ipsec.secrets:
<your local IP> <remote IP of Mikrotik system> : PSK "<Put your preshared key here>"
MikroTik Config
The following config is best done from the terminal on a MikroTik device.
Note: You can use the following config to connect two MikroTik systems. Just replicate the config below on each system you wish to connect.
/ip ipsec policy add src-address=0.0.0.0/0 dst-address=<remote IP of strongswan system> proposal=ike2 ipsec-protocols=esp /ip ipsec proposal add name="ike2" auth-algorithms=sha256,sha1 enc-algorithms=aes-256-cbc,aes-128-cbc lifetime=30m pfs-group=none /ip ipsec peer add name="<name of strongswan system>" address=<local IP> profile=ike2 exchange-mode=main send-initial-contact=yes /ip ipsec identity add peer=<remote IP of strongswan system> auth-method=pre-shared-key secret="<Put your preshared key here>" generate-policy=no /ip ipsec profile add name="ike2" hash-algorithm=sha1 enc-algorithm=aes-256,aes-192,aes-128,3des,des dh-group=modp2048,modp1024 lifetime=8h proposal-check=obey nat-traversal=no dpd-interval=2m dpd-maximum-failures=5
strongSwan to Cisco - IKEv1
Cisco IOS Config
crypto isakmp policy 10 encr aes authentication pre-share group 5 crypto isakmp key cisco address 172.16.10.2 crypto ipsec transform-set TS esp-aes esp-sha-hmac mode tunnel crypto map cmap 10 ipsec-isakmp set peer 172.16.10.2 set transform-set TS match address cryptoacl interface Ethernet0/1 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 172.16.10.1 255.255.255.0 crypto map cmap ip access-list extended cryptoacl permit ip 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
strongSwan Config
ipsec.conf
/etc/ipsec.conf:
config setup
# strictcrlpolicy=yes
# uniqueids = no
conn %default
ikelifetime=1440m
keylife=60m
rekeymargin=3m
keyingtries=1
keyexchange=ikev1
authby=secret
conn ciscoios
left=172.16.10.2 #strongswan outside address
leftsubnet=192.168.2.0/24 #network behind strongswan
leftid=172.16.10.2 #IKEID sent by strongswan
leftfirewall=yes
right=172.16.10.1 #IOS outside address
rightsubnet=192.168.1.0/24 #network behind IOS
rightid=172.16.10.1 #IKEID sent by IOS
auto=add
ike=aes128-md5-modp1536 #P1: modp1536 = DH group 5
esp=aes128-sha1 #P2
ipsec.secrets
/etc/ipsec.secrets:
172.16.10.2 172.16.10.1 : PSK cisco
strongSwan to Cisco - IKEv2
Source: [[10]]
Cisco IOS Config
crypto ikev2 proposal ikev2proposal
encryption aes-cbc-128
integrity sha1
group 5
crypto ikev2 policy ikev2policy
match fvrf any
proposal ikev2proposal
crypto ikev2 keyring keys
peer strongswan
address 172.16.10.2
pre-shared-key local cisco
pre-shared-key remote cisco
crypto ikev2 profile ikev2profile
match identity remote address 172.16.10.2 255.255.255.255
authentication remote pre-share
authentication local pre-share
keyring local keys
crypto ipsec transform-set TS esp-aes esp-sha-hmac
mode tunnel
crypto map cmap 10 ipsec-isakmp
set peer 172.16.10.2
set transform-set TS
set ikev2-profile ikev2profile
match address cryptoacl
interface Ethernet0/1
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 172.16.10.1 255.255.255.0
crypto map cmap
ip access-list extended cryptoacl
permit ip 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
strongSwan Config
ipsec.conf
/etc/ipsec.conf:
config setup
# strictcrlpolicy=yes
# uniqueids = no
conn %default
ikelifetime=1440m
keylife=60m
rekeymargin=3m
keyingtries=1
keyexchange=ikev1
authby=secret
conn ciscoios
left=172.16.10.2
leftsubnet=192.168.2.0/24
leftid=172.16.10.2
leftfirewall=yes
right=172.16.10.1
rightsubnet=192.168.1.0/24
rightid=172.16.10.1
auto=add
ike=aes128-sha1-modp1536
esp=aes128-sha1
keyexchange=ikev2
ipsec.secrets
/etc/ipsec.secrets:
172.16.10.2 : PSK "cisco" 172.16.10.1 : PSK "cisco"
PPTP
Persistent SSH Tunnels
The following is how to create a persistent SSH Tunnel between two systems. This is handy if you want to secure data flowing across networks, or even setup a tunnel without messing with VPN configuration.
Create User/Generate SSH key
First you will create the user you will use for the tunnel. This will allow you to forward non-privileged ports over 1024.
Note: This user does not have a password assigned or a shell. This will prevent user logins to the system.
useradd -m -s /bin/false autossh
Now switch to the user and generate an SSH key:
su -s /bin/bash autossh cd ~ ssh-keygen -b 4096
Note: Leave password blank
Once done, exit back to your normal user shell
exit
Copy public key to target system
You will need to copy id_rsa.pub file from /home/autossh/.ssh/ to the authorized_keys file on the remote system you want to connect to for the tunnel.
Note: It is recommended that you also create a normal user on the remote system and not use root.
Install autossh
You will need to install the autossh program on the system that will initiate the SSH tunnel. Autossh automatically restarts the SSH tunnel when it exits.
apt-get install autossh
Setup script
Copy the following script, making the necessary changes as specified between the <> and place on the system that will initiate the tunnel (here we will save it as /opt/ssh-tunnel.sh):
#!/bin/sh # su -s /bin/sh autossh -c 'autossh -M 0 -N -o "ServerAliveInterval 30" -o "ServerAliveCountMax 3" -o "ExitOnForwardFailure=yes" -f -T -R localhost:<target port>:<local IP or localhost>:<local port> <user>@<domain>'
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| localhost | localhost or IP address on target system |
| <target port> | port on target system |
| <local IP or localhost> | localhost or IP address on system initiating tunnel |
| <local port> | port on system initiating tunnel |
| <user@domain> | username and domain to use when SSHing to target system |
An example of this command is:
su -s /bin/sh autossh -c 'autossh -M 0 -N -o "ServerAliveInterval 30" -o "ServerAliveCountMax 3" -o "ExitOnForwardFailure=yes" -f -T -R localhost:3306:localhost:3306 joe@blow.com'
This would allow the target (remote) system to access the local (system initiating the SSH tunnel) system's MySQL server over the tunnel.
You can also use -L to change the direction of the port forwarding from Remote to Local and have the initiating system forward data over the tunnel the the remote.
Make script executable
Make sure you mark the script as executable with:
chmod +x /opt/ssh-tunnel.sh
Tunnel at startup
To have the tunnel up when the system restarts, choose one of the following methods
rc.local
Add a line to /etc/rc.local that calls the script.
# Start AutoSSH tunnel at boot /opt/ssh-tunnel.sh
Note: You may have to enable rc.local on Ubuntu and Debian based systems via systemd. Refer to your distributions documentation for information on how to enable it.
systemd
To have the script start at boot with systemd, create the following file and add it to /etc/systemd/system/ssh-tunnel.service
ssh-tunnel.service
[Unit] Description=AutoSSH Tunnel at boot [Service] Type=oneshot ExecStart=/opt/ssh-tunnel.sh [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Enable service
To enable the service to run via systemd run:
systemctl enable ssh-tunnel.service
GRE Tunnel
GRE Tunnels
Public/Private VM tunnel
GRE tunnels are useful for connecting a VM in a private/home network to the internet via a public server/VM. The following information will connect Server A (public server) to Server B (private server), and allow requests to Server B to be passed to Server A's resources for use on the Internet.
Configuration
IP addresses
- Server A will have a public IP of 30.30.30.30/24 and the GRE interface will be assigned 192.168.168.1/30
- Server B will have a private IP of 10.0.0.50/24, a public IP of 40.40.40.40/24 and the GRE interface will be assigned 192.168.168.2/30
Ports
- Ports 22, 80 and 443 will be forwarded over the GRE tunnel
Server A (Public)
Copy the following to /etc/gre.sh
#!/bin/sh
ip tunnel add gre1 mode gre local 10.0.0.50 remote 40.40.40.40 ttl 255
ip add add 192.168.168.1/30 dev gre1
ip link set gre1 up
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.168.0/30 ! -o gre+ -j SNAT --to-source 30.30.30.30
iptables -A FORWARD -d 192.168.168.2 -m state --state NEW.ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT
iptables -A FORWARD -d 192.168.168.2 -m state --state NEW.ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -d 30.30.30.30 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 22 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.168.2
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -d 30.30.30.30 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 80 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.168.2
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -d 30.30.30.30 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 443 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.168.2
Server B (Private)
- Add the following to /etc/iproute2/rt_tables
100 GRE
- Copy the following to /etc/gre.sh
#!/bin/sh
iptunnel add gre1 mode gre local 10.0.0.50 remote 30.30.30.30 ttl 255
ip addr add 192.168.168.2/30 dev gre1
ip link set gre1 up
ip rule add from 192.168.168.0/30 table GRE
ip route add default via 192.168.168.1 table GRE
L2TP Ethernet Pseudowires
Cisco
The following configuration will setup L2TPv3 between two Cisco Routers - R1 and R2.
R1 - Router Config
pseudowire-class test encapsulation l2tpv3 ip local interface Loopback0 ip pmtu ip tos value 10 ! ! interface Loopback0 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 ! interface FastEthernet0/0.1 encapsulation dot1Q 5 xconnect 2.2.2.2 1 encapsulation l2tpv3 pw-class test ! interface FastEthernet0/0.2 encapsulation dot1Q 2 xconnect 2.2.2.2 2 encapsulation l2tpv3 pw-class test
R2 - Router Config
pseudowire-class test encapsulation l2tpv3 ip local interface Loopback0 ip pmtu ip tos value 10 ! ! interface Loopback0 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 ! ! interface FastEthernet0/1.1 encapsulation dot1Q 5 xconnect 1.1.1.1 1 encapsulation l2tpv3 pw-class test ! interface FastEthernet0/1.2 encapsulation dot1Q 2 xconnect 1.1.1.1 2 encapsulation l2tpv3 pw-class test
Linux
Create an L2TP ethernet pseudowires connection using the Linux kernel's L2TP drivers along with the ip utility.
Note: This setup does not have any security. You will need to route it over IPSEC to create a secure connection.
In this example we use separate systems to establish the tunnels across the Gateway (which represents the Internet).
Topology
| System | Network |
|---|---|
| Gateway | eth1: 1.1.1.1/30; eth2: 2.2.2.1.30 |
| Tunnel1 | eth1/l2tpeth0 (bridged); eth1: No IP configured; eth2: 1.1.1.2/30 |
| Tunnel2 | eth1/l2tpeth0 (bridged); eth1: No IP configured; eth2: 2.2.2.2/30 |
Configuration
- Enable IP forwarding on Gateway, Tunnel1 and Tunnel2 systems by running this command on each:
# echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
- Establish L3 connectivity between Tunnel1 and Tunnel2 systems:
On Tunnel1 run:
# ip route add 2.2.2.0/30 via 1.1.1.1
On Tunnel2 run:
# ip route add 1.1.1.0/30 via 2.2.2.1
Check to make sure both sides can ping each other:
#tunnel1:~# ping -c1 2.2.2.2
PING 2.2.2.2 (2.2.2.2) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 2.2.2.2: icmp_req=1 ttl=63 time=1.03 ms
#tunnel2:~# ping -c1 1.1.1.2
PING 1.1.1.2 (1.1.1.2) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 1.1.1.2: icmp_req=1 ttl=63 time=1.20 ms
- Load L2TPv3 ethernet pseudowire module on Tunnel1 and Tunnel2 systems:
# modprobe l2tp_eth
- Configure l2tp interface on Tunnel1:
# ip l2tp add tunnel tunnel_id 1000 peer_tunnel_id 2000 encap udp local 1.1.1.2 remote 2.2.2.2 udp_sport 6000 udp_dport 5000 # ip l2tp add session tunnel_id 1000 session_id 3000 peer_session_id 4000
- Check configuration of tunnel on Tunnel1 system:
# ip l2tp show tunnel
Tunnel 1000, encap UDP From 1.1.1.2 to 2.2.2.2 Peer tunnel 2000 UDP source / dest ports: 6000/5000 UDP checksum: disabled
# ip l2tp show session
Session 3000 in tunnel 1000 Peer session 4000, tunnel 2000 interface name: l2tpeth0 offset 0, peer offset 0
- Configure l2tp interface on Tunnel2:
# ip l2tp add tunnel tunnel_id 2000 peer_tunnel_id 1000 encap udp local 2.2.2.2 remote 1.1.1.2 udp_sport 5000 udp_dport 6000 # ip l2tp add session tunnel_id 2000 session_id 4000 peer_session_id 3000
- Check configuration of tunnel on Tunnel2 system:
# ip l2tp show tunnel
Tunnel 2000, encap UDP From 2.2.2.2 to 1.1.1.2 Peer tunnel 1000 UDP source / dest ports: 5000/6000 UDP checksum: disabled
# ip l2tp show session
Session 4000 in tunnel 2000 Peer session 3000, tunnel 1000 interface name: l2tpeth0 offset 0, peer offset 0
- Check MTU of newly created interfaces
# ip a s dev l2tpeth0
l2tpeth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1488 qdisc noop state DOWN qlen 1000
link/ether 1a:8f:6e:04:3f:a3 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
- Adjust MTU and enforce MSS on eth1 on both Tunnel1 and Tunnel2 systems to prevent fragmentation that can cause issues:
# ip link set eth1 mtu 1446 # iptables -A FORWARD -p tcp --tcp-flags SYN,RST SYN -m tcpmss --mss 1406:1536 -j TCPMSS --set-mss 1406
- Install bridge-utils on Tunnel1 and Tunnel2 systems:
# apt-get install bridge-utils
- Bridge the L2TP interface to eth1 on both the Tunnel1 and Tunnel2 systems so that is can communicate over the network:
# brctl addbr l2tp # brctl addif l2tp eth1 l2tpeth0
- Check bridge configuration on Tunnel1 and Tunnel2 systems:
# brctl show
bridge name bridge id STP enabled interfaces l2tp 8000.1a8f6e043fa3 no eth1 l2tpeth0
- Turn up the new l2tpeth0 interface on Tunnel1 and Tunnel2 systems so that it can be used:
# ip l set dev l2tpeth0 up # ip l set dev l2tp up
Assuming you've done everything correctly here, you should now be able to use the Tunnel1 and Tunnel2 systems to send traffic over the same subnet on each side.
Example:
- Using the setup above, assume you have two additional systems setup.
- Computer1 is connected to Tunnel1. No gateway set (not needed for an L2 link).
- Computer1 has eth1 configured with 192.168.0.3/24
- Computer2 is connected to Tunnel2. No gateway set (not needed for an L2 link).
- Computer 2 has eth1 configured wtih 192.168.0.4/24
- Do a ping test to make sure Computer1 can talk to Computer2 through the l2tp link:
# ping -c5 192.168.0.4
64 bytes from 192.168.0.4: icmp_req=1 ttl=64 time=3.85 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.0.4: icmp_req=2 ttl=64 time=1.93 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.0.4: icmp_req=3 ttl=64 time=1.91 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.0.4: icmp_req=4 ttl=64 time=1.87 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.0.4: icmp_req=5 ttl=64 time=1.89 ms
- Successful output means that Computer1 can talk to Computer2 over the l2tp link since you're created a L2 link between each system. Both computers act as if they are on the same local network segment, unaware of the L2TP connection over the Gateway via the Tunnels.
The path that data will travel is:
Computer1 -> Tunnel1 -> Gateway -> Tunnel2 -> Computer2 Computer1 <- Tunnel1 <- Gateway -< Tunnel2 -< Computer2
NOTE: THERE IS NO ENCRYPTION WITH AN L2TP TUNNEL. ALL LAYER 2 DATA THAT IS VISIBLE TO EACH SIDE OF THE TUNNEL WILL NORMALLY BE SENT OVER THE LINK AND BE SEEN BY THE OTHER SIDE.
Between Cisco and Linux
You can use L2TPv3 between Cisco and Linux utilizing the following script from Leif Sawyer.
- Script repository: https://github.com/akhepcat/Miscellaneous
- Direct download link: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/akhepcat/Miscellaneous/master/l2tpv3-cisco.sh
This script will bring up the Linux side of the connection and generate the Cisco side config.
Configuration
- Edit the variables TUNNEL_ID, SESSION_ID, LOCAL, and REMOTE to values that are suitable for your environment.
Commands
- Start the tunnel with l2tpv3-cisco.sh start
- Stop the tunnel with l2tpv3-cisco.sh stop
- Restart the tunnel with l2tpv3-cisco.sh restart
- Generate Cisco config with l2tpv3-cisco.sh config
l2tpv3-cisco.sh
#!/bin/bash # (c) 2020 Leif Sawyer # License: GPL 3.0 (see https://github.com/akhepcat/) # Permanent home: https://github.com/akhepcat/Miscellaneous/ # Direct download: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/akhepcat/Miscellaneous/master/l2tpv3-cisco.sh # # using l2tpV3 between linux and cisco is sometimes weird. # this script is how I get the linux side up. # This will also auto-generate the cisco-side config. ################################ TUNNEL_ID=101 REMOTE_TUNNEL_ID=${TUNNEL_ID} SESSION_ID=101 REMOTE_SESSION_ID=${SESSION_ID} LOCAL=10.1.1.1 REMOTE=10.100.100.1 ################################ PATH=/sbin:$PATH IPV=$(ip -V | sed 's/.*-ss//') if [ ${IPV:-0} -lt 130716 ] then echo "Please install a newer version of iproute2 ( 3.10 or (>= 2013-07-16))" echo " from https://www.kernel.org/pub/linux/utils/net/iproute2/" exit fi modules() { for module in l2tp_core l2tp_netlink l2tp_eth l2tp_ip do modprobe $i done } tunnel_up() { ip l2tp add tunnel remote ${REMOTE} local ${LOCAL} tunnel_id $TUNNEL_ID peer_tunnel_id $REMOTE_TUNNEL_ID encap ip ip l2tp add session tunnel_id $TUNNEL_ID session_id $SESSION_ID peer_session_id $REMOTE_SESSION_ID l2spec_type none ip link set l2tpeth0 up mtu 1488 iptables -A FORWARD -p tcp --tcp-flags SYN,RST SYN -m tcpmss --mss 1448:1536 -j TCPMSS --set-mss 1448 } tunnel_down() { iptables -D FORWARD -p tcp --tcp-flags SYN,RST SYN -m tcpmss --mss 1448:1536 -j TCPMSS --set-mss 1448 ip link set l2tpeth0 down ip l2tp del session tunnel_id $TUNNEL_ID session_id $SESSION_ID ip l2tp del tunnel tunnel_id $TUNNEL_ID } cisco_config() { cat <<EOF ! Global config ! pseudowire-class Linux-L2TP encapsulation l2tpv3 interworking ethernet protocol none ip local interface $REMOTE ip pmtu ip tos value 41 ip ttl 100 ! ! Interface config ! interface \$L2interface xconnect $LOCAL $REMOTE_TUNNEL_ID encapsulation l2tpv3 manual pw-class Linux-L2TP l2tp id $SESSION_ID $REMOTE_SESSION_ID EOF } case $1 in start|up) tunnel_up ;; stop|down) tunnel_down ;; restart|reload) stop; start ;; config|cisco|cisco-config) cisco_config ;; *) echo "$0 (start|up || stop|down || restart|reload || config|cisco|cisco-config)" ;; esac
OpenVPN
Information on OpenVPN is available from https://openvpn.org/[3]
Road Warrior Install
"In business travel, a road warrior is a person that uses mobile devices such as tablet, laptop, smartphone and internet connectivity while traveling to conduct business. The term has often been used with regard to salespeople who travel often and who seldom are in the office. Today it is used for anyone who works outside the office and travels for business." [4]
This will walk you through setting up the OpenVPN Road Warrior install for Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS and Fedora.
Installation
- Run the script and follow the on-screen prompts:
wget https://git.io/vpn -O openvpn-install.sh && bash openvpn-install.sh
- Example install using the defaults (installed on Ubuntu 20.04.2 LTS VM):
Welcome to this OpenVPN road warrior installer!
Which protocol should OpenVPN use?
1) UDP (recommended)
2) TCP
Protocol [1]:
What port should OpenVPN listen to?
Port [1194]:
Select a DNS server for the clients:
1) Current system resolvers
2) Google
3) 1.1.1.1
4) OpenDNS
5) Quad9
6) AdGuard
DNS server [1]:
Enter a name for the first client:
Name [client]:
OpenVPN installation is ready to begin.
Press any key to continue...
Get:1 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-security InRelease [114 kB]
Hit:2 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal InRelease
Get:3 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-updates InRelease [114 kB]
Get:4 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-backports InRelease [101 kB]
Fetched 328 kB in 1s (488 kB/s)
Reading package lists... Done
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
ca-certificates is already the newest version (20210119~20.04.1).
openssl is already the newest version (1.1.1f-1ubuntu2.4).
Suggested packages:
resolvconf openvpn-systemd-resolved easy-rsa
The following NEW packages will be installed:
openvpn
0 upgraded, 1 newly installed, 0 to remove and 0 not upgraded.
Need to get 0 B/477 kB of archives.
After this operation, 1,188 kB of additional disk space will be used.
Preconfiguring packages ...
Selecting previously unselected package openvpn.
(Reading database ... 109259 files and directories currently installed.)
Preparing to unpack .../openvpn_2.4.7-1ubuntu2.20.04.2_amd64.deb ...
Unpacking openvpn (2.4.7-1ubuntu2.20.04.2) ...
Setting up openvpn (2.4.7-1ubuntu2.20.04.2) ...
* Restarting virtual private network daemon. [ OK ]
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/openvpn.service → /lib/systemd/system/openvpn.service.
Processing triggers for man-db (2.9.1-1) ...
Processing triggers for systemd (245.4-4ubuntu3.7) ...
init-pki complete; you may now create a CA or requests.
Your newly created PKI dir is: /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki
Using SSL: openssl OpenSSL 1.1.1f 31 Mar 2020
Generating RSA private key, 2048 bit long modulus (2 primes)
......+++++
...................+++++
e is 65537 (0x010001)
Using SSL: openssl OpenSSL 1.1.1f 31 Mar 2020
Generating a RSA private key
..........................................................................................................................................+++++
....+++++
writing new private key to '/etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki/easy-rsa-2749.6tj7Mb/tmp.fSqcnR'
-----
Using configuration from /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki/easy-rsa-2749.6tj7Mb/tmp.TS5dnM
Check that the request matches the signature
Signature ok
The Subject's Distinguished Name is as follows
commonName :ASN.1 12:'server'
Certificate is to be certified until Jul 10 05:27:40 2031 GMT (3650 days)
Write out database with 1 new entries
Data Base Updated
Using SSL: openssl OpenSSL 1.1.1f 31 Mar 2020
Generating a RSA private key
............................+++++
..............+++++
writing new private key to '/etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki/easy-rsa-2824.Fx4J3A/tmp.tlGKns'
-----
Using configuration from /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki/easy-rsa-2824.Fx4J3A/tmp.dVVyTl
Check that the request matches the signature
Signature ok
The Subject's Distinguished Name is as follows
commonName :ASN.1 12:'client'
Certificate is to be certified until Jul 10 05:27:40 2031 GMT (3650 days)
Write out database with 1 new entries
Data Base Updated
Using SSL: openssl OpenSSL 1.1.1f 31 Mar 2020
Using configuration from /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki/easy-rsa-2880.kL0wa3/tmp.uyyWGn
An updated CRL has been created.
CRL file: /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki/crl.pem
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/openvpn-iptables.service → /etc/systemd/system/openvpn-iptables.service.
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/openvpn-server@server.service → /lib/systemd/system/openvpn-server@.service.
Finished!
The client configuration is available in: /root/client.ovpn
New clients can be added by running this script again.
Add a user
To add a new user, run the openvpn-install.sh script again and select option 1 - Add a new client
# bash openvpn-install.sh
OpenVPN is already installed.
Select an option:
1) Add a new client
2) Revoke an existing client
3) Remove OpenVPN
4) Exit
Option: 1
- You will be prompted for a name, in this example we use client2
Provide a name for the client: Name: client2 Using SSL: openssl OpenSSL 1.1.1f 31 Mar 2020 Generating a RSA private key ....................................................+++++ ....+++++ writing new private key to '/etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki/easy-rsa-4310.cmbMtC/tmp.MMKA2C' ----- Using configuration from /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki/easy-rsa-4310.cmbMtC/tmp.l84eev Check that the request matches the signature Signature ok The Subject's Distinguished Name is as follows commonName :ASN.1 12:'client2' Certificate is to be certified until Jul 10 05:41:10 2031 GMT (3650 days) Write out database with 1 new entries Data Base Updated client2 added. Configuration available in: /root/client2.ovpn
- Copy the configuration file above to your client to use it with OpenVPN
Remove a user
To add a remove a user, run the openvpn-install.sh script again and select option 2 - Revoke an existing client
# bash openvpn-install.sh
OpenVPN is already installed.
Select an option:
1) Add a new client
2) Revoke an existing client
3) Remove OpenVPN
4) Exit
Option: 2
- You will be presented with a list of configured users to remove. We will choose client2 for this example.
Select the client to revoke:
1) client
2) client2
Client: 2
Confirm client2 revocation? [y/N]: Y
Using SSL: openssl OpenSSL 1.1.1f 31 Mar 2020
Using configuration from /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki/easy-rsa-4407.i66z91/tmp.iS3gWM
Revoking Certificate 05D02E0DF2A242398233588721BB75E0.
Data Base Updated
Using SSL: openssl OpenSSL 1.1.1f 31 Mar 2020
Using configuration from /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki/easy-rsa-4444.LpkzMp/tmp.03Azaw
An updated CRL has been created.
CRL file: /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki/crl.pem
client2 revoked!
Uninstall
- To uninstall, run the openvpn-install.sh script again and select option 3 - Remove OpenVPN
Confirm OpenVPN removal? [y/N]:
- When prompted answer Y to start the removal
Removed /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/openvpn-iptables.service.
Removed /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/openvpn-server@server.service.
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
The following package was automatically installed and is no longer required:
libpkcs11-helper1
Use 'apt autoremove' to remove it.
The following packages will be REMOVED:
openvpn*
0 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 1 to remove and 0 not upgraded.
After this operation, 1,188 kB disk space will be freed.
(Reading database ... 109344 files and directories currently installed.)
Removing openvpn (2.4.7-1ubuntu2.20.04.2) ...
Processing triggers for man-db (2.9.1-1) ...
(Reading database ... 109265 files and directories currently installed.)
Purging configuration files for openvpn (2.4.7-1ubuntu2.20.04.2) ...
Processing triggers for systemd (245.4-4ubuntu3.7) ...
OpenVPN removed!
TINC
Tinc is an open-source, self-routing, mesh networking protocol, used for compressed, encrypted, virtual private networks.
Tinc is available for FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, Dragonfly BSD, Mac OS X, Linux, Microsoft Windows, Solaris, IOS (jailbroken only), and Android with full support for IPv6.
You can download tinc for *nix and Windows systems from https://www.tinc-vpn.org/[5]
The tinc website includes many examples on common setups. They can be found at https://www.tinc-vpn.org/examples/
Standard tinc setup
Tinc can be setup in a mesh network with multiple systems.
Note: You can setup tinc with just two systems using these instructions and adjusting the steps accordingly.
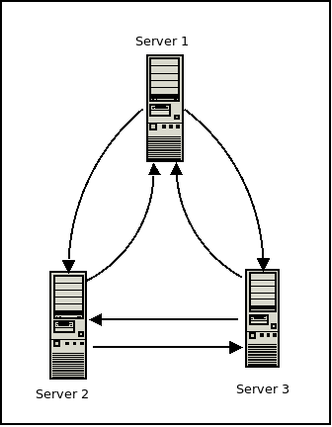
For this setup we will have three hosts called Server 1, Server 2, and Server 3. The following is a brief synopsis of the network config for each:
VPN NAME: NoMoreSecrets
SERVER 1:
public ip: 1.1.1.100 vpn ip: 10.0.0.1 connects to: server 2, server 3
SERVER 2:
public ip: 1.1.2.100 vpn ip: 10.0.0.2 connects to: server 1, server 3
SERVER 3:
public ip: 1.1.3.100 vpn ip: 10.0.0.3 connects to: server 1, server 2
The following directory tree will be present on all three hosts for this setup:
/etc
└── tinc
└── NoMoreSecrets
├── hosts
│ ├── server1
│ ├── server2
│ └── server3
├── rsa_key.priv
├── tinc.conf
├── tinc-down
└── tinc-up
FreeBSD Note
FreeBSD will use the /usr/local/etc/tinc directory structure instead of the Linux /etc/tinc as shown above. Adjust the paths below accordingly. Additionally, the tinc-up and tinc-down files will differ. See the section below the Server 3 example for notes on these differences.
Individual node setup and configuration
All servers used in this example will be running Ubuntu 18.04.
Server1
- Install tinc
apt install tinc -y
- Create directories
mkdir -p /etc/tinc/NoMoreSecrets/hosts/
Create the following files:
- /etc/tinc/NoMoreSecrets/hosts/server1:
Address = 1.1.1.100 Subnet = 10.0.0.1
- /etc/tinc/NoMoreSecrets/tinc.conf:
Name = server1 Interface = tun0 AddressFamily = ipv4 ConnectTo = server2 ConnectTo = server3
- /etc/tinc/NoMoreSecrets/tinc-up:
#!/bin/sh ip link set $INTERFACE up ip addr add 10.0.0.1/32 dev $INTERFACE ip route add 10.0.0.0/24 dev $INTERFACE
- /etc/tinc/NoMoreSecrets/tinc-down:
#!/bin/sh ip route del 10.0.0.0/24 dev $INTERFACE ip addr del 10.0.0.1/32 dev $INTERFACE ip link set $INTERFACE down
Server2
- Install tinc
apt install tinc -y
- Create directories
mkdir -p /etc/tinc/NoMoreSecrets/hosts/
Create the following files:
- /etc/tinc/NoMoreSecrets/hosts/server2:
Address = 1.1.2.100 Subnet = 10.0.0.2
- /etc/tinc/NoMoreSecrets/tinc.conf:
Name = server2 Interface = tun0 AddressFamily = ipv4 ConnectTo = server1 ConnectTo = server3
- /etc/tinc/NoMoreSecrets/tinc-up:
#!/bin/sh ip link set $INTERFACE up ip addr add 10.0.0.2/32 dev $INTERFACE ip route add 10.0.0.0/24 dev $INTERFACE
- /etc/tinc/NoMoreSecrets/tinc-down:
#!/bin/sh ip route del 10.0.0.0/24 dev $INTERFACE ip addr del 10.0.0.2/32 dev $INTERFACE ip link set $INTERFACE down
Server3
- Install tinc
apt install tinc -y
- Create directories
mkdir -p /etc/tinc/NoMoreSecrets/hosts/
Create the following files:
- /etc/tinc/NoMoreSecrets/hosts/server3:
Address = 1.1.3.100 Subnet = 10.0.0.3
- /etc/tinc/NoMoreSecrets/tinc.conf:
Name = server3 Interface = tun0 AddressFamily = ipv4 ConnectTo = server1 ConnectTo = server2
- /etc/tinc/NoMoreSecrets/tinc-up:
#!/bin/sh ip link set $INTERFACE up ip addr add 10.0.0.3/32 dev $INTERFACE ip route add 10.0.0.0/24 dev $INTERFACE
- /etc/tinc/NoMoreSecrets/tinc-down:
#!/bin/sh ip route del 10.0.0.0/24 dev $INTERFACE ip addr del 10.0.0.3/32 dev $INTERFACE ip link set $INTERFACE down
FreeBSD Note
The tinc-up and tinc-down files will differ from those listed above as follows:
- /usr/local/etc/tinc/NoMoreSecrets/tinc-up:
#!/bin/sh ifconfig "$INTERFACE" up ifconfig "$INTERFACE" inet 10.0.0.3 netmask 255.255.255.255 route add -net 10.0.0.0 10.0.0.3
Note: Substitute route add -host <remote tinc ip> <local tinc ip> in place of the last line above for a two node setup
- /usr/local/etc/tinc/NoMoreSecrets/tinc-down:
#!/bin/sh ifconfig "$INTERFACE" destroy exit
Create keypair
- On all servers create public/private keypair with:
tincd -n NoMoreSecrets -K4096
Synchronize host files
- Synchronize host files with public keys between all three servers with rsync:
- From Server1:
rsync -avz /etc/tinc/NoMoreSecrets/hosts/ server2:/etc/tinc/NoMoreSecrets/hosts/ rsync -avz /etc/tinc/NoMoreSecrets/hosts/ server3:/etc/tinc/NoMoreSecrets/hosts/
- From Server2:
rsync -avz /etc/tinc/NoMoreSecrets/hosts/ server1:/etc/tinc/NoMoreSecrets/hosts/ rsync -avz /etc/tinc/NoMoreSecrets/hosts/ server3:/etc/tinc/NoMoreSecrets/hosts/
- From Server3:
rsync -avz /etc/tinc/NoMoreSecrets/hosts/ server1:/etc/tinc/NoMoreSecrets/hosts/ rsync -avz /etc/tinc/NoMoreSecrets/hosts/ server2:/etc/tinc/NoMoreSecrets/hosts/
- On all servers set the executable bit on the tinc-up and tinc-down scripts
chmod +x /etc/tinc/NoMoreSecrets/tinc-up chmod +x /etc/tinc/NoMoreSecrets/tinc-down
Start tinc
Linux:
- On all servers enable and start tinc
systemctl enable tinc@NoMoreSecrets systemctl start tinc@NoMoreSecrets
FreeBSD:
You will need to ensure that tincd is properly configured on /etc/rc.conf before you attempt to start it:
- Add the following to your /etc/rc.conf:
#tinc tincd_enable="YES" tincd_cfg="NoMoreSecrets" tincd_flags="-d 2 -L"
- Start tinc with:
service tincd start
Once tinc is up and running on all three servers you should be able to communicate over the 10.0.0.0/24 network.
Since this is a mesh network, if direct communication between two nodes drops, tinc will route all traffic through the remaining node until direct communication is restored.
Troubleshooting
- Check tinc logs to see what the error shown is. Refer to official documentation at https://www.tinc-vpn.org/docs/
- Check firewall on both hosts to make sure port 655 is being accepted.
- Check IP on Address line of hosts to ensure they are correct.
- Check IP on Subnet line of hosts files to ensure they are correct.
Simplified tinc 1.1 Windows setup
Examples on how to setup tinc 1.1 on Windows as either a server or client.
Server side config
- Download tinc
- Install tinc
- Open command prompt and type the following:
cd "C:\Program Files\tinc" tinc -n vpn init master tinc -n vpn add subnet 10.0.1.1 tinc -n vpn add address=public.domain-or-ip cd tap-win64 addtap.bat netsh interface ipv4 show interfaces (Note disconnected interface. May be called Ethernet 2) netsh interface set interface name = "Ethernet 2" newname = "tinc" netsh interface ip set address "tinc" static 10.0.1.1 255.255.255.0 netsh interface ipv4 show config (Should create a tinc interface with IP and subnet) cd ..
To start tinc:
tincd -n vpn
To invite clients:
tinc -n vpn invite client1
Client side config
- Download tinc
- Install tinc
- Open command prompt and type the following:
cd "C:\Program Files\tinc" tinc join <invite-url> tinc -n vpn add subnet 10.0.1.2 cd tap-win64 addtap.bat netsh interface ipv4 show interfaces (Note disconnected interface. May be called Ethernet 2) netsh interface set interface name = "Ethernet 2" newname = "tinc" netsh interface ip set address "tinc" static 10.0.1.2 255.255.255.0 cd ..
To test connection:
tincd -n vpn -D -d3
To run tinc as service:
tincd -n vpn
Notes
Tinc will automatically register itself as a service when started without -D or --no-detach option.
Calling tinc with -k or --kill option will cause it to automatically unregister itself.
SOCAT
SOCAT can be used to create a simple virtual network between two hosts using UDP and TUN devices.
Note: It is possible to use TCP for this as well, but without the nodelay option it might cause problems. You can also replace UDP with DTLS to add security to the connection.
- IP addresses used in this example:
| Host | Address | Mask |
|---|---|---|
| Physical server address | 1.2.3.4 | N/A |
| Physical client address | N/A | N/A |
| TUN device on server | 192.168.255.1 | 255.255.255.0 |
| TUN device on client | 192.168.255.2 | 255.255.255.0 |
Note: UDP connections will use PORT 11443.
Create TUN devices
- TUN Server
socat -d -d UDP-LISTEN:11443,reuseaddr TUN:192.168.255.1/24,up
- TUN Client
socat UDP:1.2.3.4:11443 TUN:192.168.255.2/24,up
Executing these two commands will result in a connection being established from the client to the server via TUN devices.
Troubleshooting
The following are common errors that you may encounter when using SOCAT to create a VPN.
- Missing TUN/TAP Support
... E unknown device/address "tun"
The SOCAT binary probably does not provide TUN/TAP support. Reasons include not using Linux and using an older version of SOCAT.
- Missing Kernel Support
,,, E open("/dev/net/tun", 02, 0666): No such file or directory
This incidates that your kernel does not have TUN/TAP support compiled in.
- TUN Cloning Device Permissions
... E open("/dev/net/tun", 02, 0666): Permission denied
This indicates that you do not have sufficient permission to read or write to the TUN cloning device. Check the device's permssions and ownership.
SoftEther
SoftEther VPN is an Open-Source Free Cross-platform Multi-protocol VPN Program, that is an academic project from the University of Tsukuba in Japan.
You can download SoftEther for FreeBSD, Linux, Mac, Solaris, and Windows from https://www.softether.org/[6]
Features
- SSL-VPN tunnelling on HTTPS to pass though NAT and firewalls
- Revolutionary VPN over ICMP and VPN over DNS featuers
- Ethernet-bridging (L2) and IP-routing (L3) over VPN.
- Embedded dynamic-DNS and NAT-traversal
- SSL-VPN (HTTPS) and support for 6 major VPN protocols: OpenVPN, IPSEC, L2TP, MS-SSTP, L2TPv3, and EtherIP)
Cisco L2TPv3
Use the setup of SoftEther here as a guide for an L2TPv3 connection to a Cisco device.
SoftEther settings
Now make the following adjustments to the IPSEC/L2TPv3 settings shown there:
- Under IPSEC/L2TP setting select the checkbox for Enable EtherIP/L2TPv3 over IPsec Server Function
- Select EtherIP / L2TP Detail Settings
- ISAKMP Phase 1 ID: Specify local IP address of Cisco device here
- Fill in username/password settings
- Under Virtual Hub management
- Select Virtual NAT and virtual DHCP server function
- Secure NAT settings wtill be used to set Virtual DHCP server settings
| Type | Port # |
|---|---|
| UDP | 500 |
| UDP | 4500 |
| UDP | 1701 |
- Encryption: If you have an issue with using AES during your initial testing, try using DES or 3DES. Once you have the connection established try switching to a more secure algorithm.
Cisco config
And then use the following config below on your Cisco device instead of what is listed on the SoftEther site to get L2TPv3 working:
| Local IP addess | Peer IP (SoftEther Public IP) | Pre-shared key |
|---|---|---|
| 192.168.100.100 (ISAKMP Phase 1 ID) | 1.1.1.100 | CHANGEME |
- Note: By default Cisco may have NAT-Traversal enabled. This settings is not required.
- Specify the L2TPv3 settings and interface (change FastEterhnet0/0 to match your device's interface).
pseudowire-class L2TPv3 encapsulation l2tpv3 ip local interface FastEthernet0/0
- Note: You can chance the pseudowire-class interface's name from L2TPv3 to something more descriptive if you want.
- ISAKMP settings:
crypto isakmp policy 1 encr aes 256 authentication pre-share group 2 crypto isakmp key CHANGEME address 1.1.1.100 crypto isakmp keepalive 10 periodic
Note: You can use AES 256 encryption here. DH group uses type 2 1024 bit encryption.
- IPSEC settings:
crypto ipsec transform-set IPSEC esp-3des esp-sha-hmac mode transport crypto ipsec fragmentation after-encryption
Note: 3des is being used here in this example. If you put this tunnel into production make sure you change the cipher used to AES!!!
- Cryptographic map:
crypto map MAP 1 ipsec-isakmp set peer 1.1.1.100 set transform-set IPSEC match address IPSEC_MATCH_RULE
- Interface configuration
interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 192.168.100.100 255.255.255.0 no ip proxy-arp duplex auto speed auto crypto map MAP
Note: FastEthernet0/0 uses the local IP address specified above and has the crypto map applied.
- Use FastEthernet0/1 as the interface for the tunnel
interface FastEthernet0/1 no ip address duplex auto speed auto no cdp enable xconnect 1.1.1.100 1 encapsulation l2tpv3 pw-class L2TPv3 bridge-group 1
- Access list:
ip access-list extended IPSEC_MATCH_RULE permit 115 any any
- Now connect a device to FastEthernet0/1. It should get a DHCP lease from SoftEther and be on the network.
Troubleshooting
To troubleshoot the tunnel use the following commands:
debug crypt isakmp debug crypt ipsec debug l2tp all
- Show ISAKMP SA status:
#show crypto isakmp sa
IPv4 Crypto ISAKMP SA
dst src state conn-id status
1.1.1.100 192.168.100.100 QM_IDLE 1011 ACTIVE
IPv6 Crypto ISAKMP SA
・IPSec
#show crypto ipsec sa
interface: FastEthernet0/0
Crypto map tag: MAP, local addr 192.168.100.100
protected vrf: (none)
local ident (addr/mask/prot/port): (0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0/115/0)
remote ident (addr/mask/prot/port): (0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0/115/0)
current_peer 1.1.1.100 port 4500
PERMIT, flags={origin_is_acl,}
#pkts encaps: 54342, #pkts encrypt: 54342, #pkts digest: 54342
#pkts decaps: 179917, #pkts decrypt: 179917, #pkts verify: 179917
#pkts compressed: 0, #pkts decompressed: 0
#pkts not compressed: 0, #pkts compr. failed: 0
#pkts not decompressed: 0, #pkts decompress failed: 0
#send errors 23, #recv errors 0
local crypto endpt.: 192.168.100.100, remote crypto endpt.: 1.1.1.100
path mtu 1500, ip mtu 1500, ip mtu idb FastEthernet0/0
current outbound spi: 0x48E82D7A(1223175546)
PFS (Y/N): N, DH group: none
inbound esp sas:
spi: 0x1B68FD22(459865378)
transform: esp-3des esp-sha-hmac ,
in use settings ={Tunnel UDP-Encaps, }
conn id: 2107, flow_id: NETGX:107, sibling_flags 80000046, crypto map: MAP
sa timing: remaining key lifetime (k/sec): (4386973/1557)
IV size: 8 bytes
replay detection support: Y
Status: ACTIVE
inbound ah sas:
inbound pcp sas:
outbound esp sas:
spi: 0x48E82D7A(1223175546)
transform: esp-3des esp-sha-hmac ,
in use settings ={Tunnel UDP-Encaps, }
conn id: 2108, flow_id: NETGX:108, sibling_flags 80000046, crypto map: MAP
sa timing: remaining key lifetime (k/sec): (4386975/1557)
IV size: 8 bytes
replay detection support: Y
Status: ACTIVE
outbound ah sas:
outbound pcp sas:
- Check L2TP session:
#show l2tp session
L2TP Session Information Total tunnels 1 sessions 1
LocID RemID TunID Username, Intf/ State Last Chg Uniq ID
Vcid, Circuit
23239**** 1900**** 2306***** 1, Fa0/1 est 01:32:52 1
- Check L2TP tunnel:
L2TP Tunnel Information Total tunnels 1 sessions 1
LocTunID RemTunID Remote Name State Remote Address Sessn L2TP Class/
Count VPDN Group
230**** 1 ******* est 1.1.1.100 1 l2tp_default_cl
Note: If you use AES for IPSEC it will become TunID 0.
WireGuard
WireGuard can be downloaded from https://www.wireguard.com/[7]
Road Warrior Install
"In business travel, a road warrior is a person that uses mobile devices such as tablet, laptop, smartphone and internet connectivity while traveling to conduct business. The term has often been used with regard to salespeople who travel often and who seldom are in the office. Today it is used for anyone who works outside the office and travels for business." [4]
This will walk you through setting up the WireGuard Road Warrior install for Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS and Fedora.
Installation
- Run the script and follow the on-screen prompts:
wget https://git.io/wireguard -O wireguard-install.sh && bash wireguard-install.sh
- You can run it again to add/remove users or completely uninstall WireGuard
Mikrotik Wireguard Road Warrior Config
From: https://forum.mikrotik.com/viewtopic.php?t=174417#[8]
The following information will show you how to setup a Mikrotik Wireguard server with Road Warrior clients.
Network topology
The network used in this examples is 192.168.66.0/24. A Mikrotik device will be the server and client can be any device running the Wireguard software.
| System | IP Address |
|---|---|
| Wireguard server | 192.168.66.1 |
| Wireguard client(s) | 192.168.66.[2-254] |
Mikrotik Configuration
# a private and public key will be automatically generated when adding the wireguard interface
/interface wireguard
add listen-port=13231 mtu=1420 name=wireguard1
/interface wireguard peers
# the first client added here is ipv4 only
add allowed-address=192.168.66.2/32 interface=wireguard1 public-key="*** replace-with-public-key-of-first-client ***"
# this client is dual stack - public IPv6 should be used - replace 2001:db8:cafe:beef: with one of your /64 prefixes.
add allowed-address=192.168.66.3/32,2001:db8:cafe:beef::3/128 interface=wireguard1 public-key="*** replace-with-public-key-of-second-client-dual-stack ***"
/ip address
add address=192.168.66.1/24 interface=wireguard1 network=192.168.66.0
/ipv6 address
add address=2001:db8:cafe:beef::1/64 interface=wireguard1
Client configuration
Interface: (whatever name you want to specify)
Public key: the client should automatically generate this - add this to the server above replacing "replace-with-public-key-of-second-client-dual-stack"
Addresses: 192.168.66.3/24,2001:db8:cafe:beef::3/64 (note these are different subnet masks than in the server config)
DNS servers: as desired - if you want to use the wireguard server for dns, specify 192.168.66.1
Peer:
Public key - get the public key from the wireguard interface on the Mikrotik device and place here
Endpoint - mydyndns.whatever:13231
Allowed IPs: 0.0.0.0/0, ::/0
This client configuration will result in all traffic being forwarded via the Mikrotik Wireguard server. You will need to ensure:
- Create an input chain firewall rule to allow UDP traffic in on port 13231
/ip firewall filter add action=accept chain=input comment="Allow Wireguard" dst-port=13231 protocol=udp
- Ensure the Mikrotik firewall is allowing traffic from 192.168.66.0/24 and that you are NATing this traffic. If your device is based off the default Mikrotik config and using the LAN interface list, you can add the Wireguard interface to this list to allow traffic through and NATing it as it leaves your network. Otherwise, you will need to modify your configuration accordingly.
Get/Set Wireguard Peers
- Get Mikrotik Wireguard peers list
/interface wireguard peers print
- Set Mikrotik Wireguard peers list
/interface wireguard peers set <ID> allowed-addresses=whatever,whateverelse
VPNC
VPNC [9] is an open-source VPN client.
| System |
|---|
| Cisco VPN concentrator 3000 Series |
| Cisco IOS routers |
| Cisco PIX / ASA Security Appliances |
| Juniper/Netscreen |
- And is available for the following operating systems:
| Name |
|---|
| Linux |
| FreeBSD |
| OpenBSD |
| NetBSD |
| DragonFly BSD |
| Darwin / Mac OS X |
| Solaris |
| Windows / Cygwin |
- Supported Authentications: Hybrid, Pre-Shared-Key + XAUTH, Pre-Shared-Key
- Supported IKE DH-Groups: dh1, dh2, dh5
- Supported Hash Algo (IKE/IPSEC): md5, sha1
- Supported Encryptions (IKE/IPSEC): (null), (1des), 3des, aes128, aes192, aes256
- Perfect Forward Secrecy: nopfs, dh1, dh2, dh5
Installation
To install VPNC on Debian based distributions:
sudo apt-get install vpnc
Configuration
Edit the default config file as follows (substitute your own name if you want to name the connection instead of using default. You will use this name as @<name> when calling vpnc.)
- Edit /etc/vpnc/default.conf.
IPSec gateway <VPNC server IP or FQDN> IPSec id AMPRNET IPSec secret EzAsARDC Xauth username YOUR-CALLSIGN Xauth password _YOUR_PASSWORD_HERE_
Starting the VPN
Use one fo the following commands to start your VPNC based VPN connection.
- This command would run VPNC using /etc/vpnc/default.conf, if it exists. If it does not, it would prompt for the connection information:
sudo vpnc
- This would run VPNC using /etc/vpnc/external.conf, if it exists.
sudo vpnc external
Starting at boot
You can start your VPNC based VPN connection at boot using one of the following methods.
/etc/rc.local
This is the simplest way and does not involve creating init scripts or systemd service files.
Add a line such as the following into your /etc/rc.local file:
vpnc
systemd
To control from systemd:
- Edit /usr/lib/systemd/system/vpnc@.service
[Unit] Description=VPNC connection to %i Wants=network-online.target After=network.target network-online.target [Service] Type=forking ExecStart=/usr/bin/vpnc --pid-file=/run/vpnc@%i.pid /etc/vpnc/%i.conf PIDFile=/run/vpnc@%i.pid [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
- Enable default VPNC configuration to be managed by systemd:
systemctl enable vpnc
- Start default VPNC connection with systemd:
systemctl start vpnc
Note: If you have multiple VPNC configurations or chose to name your config, you will substitute vpnc for vpnc@<config name>.
Other
Any other information that doesn't fit elsewhere.
Ham Radio VPN Providers
The following is a table of providers who offer free VPN connections to licensed Ham Radio operators.
Note: No commercial advertisements or pay services are allowed or permitted. Adding them will get your account removed and/or IP address banned.
| System | Contact | Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| w9cr.net | Bryan Fields, W9CR (bryan@bryanfields.net) | VPNC | Used as a means to get public IP's directly on nodes, bypassing NAT444 and man-in-the-middle IAX level filtering. Provides 44net public IP space. Include your callsign in the details. |
| AMPRNet VPN | https://wiki.ampr.org/wiki/AMPRNet_VPN | OpenVPN | AMPRNet VPN is an experimental method to access the AMPRNet using a VPN from anywhere on the Internet. The VPN is openly available to any amateur radio operators who have successfully applied for an X.509 certificate from one of the listed Certificate Authorities. |
Firewall
Information regarding firewall setup as related to the VPN configs above.
Linux
The following script can be used to setup a basic firewall on a Linux based system using iptables.
Supports IPv4 and IPv6. Comment out the parts that are not need with a # or optionally delete them.
Note: While this supports IPv6, some of the rules listed were only done for IPv4. You'll need to make the necessary changes to have IPv6 protected as well. While the parameters listed for IPv4 should work you should refer to the ip6tables man page if you have any issues.
#!/bin/bash #Modify to match your network interface INET_IF=eth0 #IPv4 #Edit IP address below to match the IP and netmask of the system or subnet you want to allow access to #"Management only" services. Add or remove as needed. Make sure to update the ManagementFilterV4 with #the changes System1="XX.XX.XX.XX/YY" System2="XX.XX.XX.XX/YY" ManagementFilterV4=$System1,$System2 #IPv6 #Edit IP address below to match the IP and netmask of the system or subnet you want to allow access to #"Management only" services. Add or remove as needed. Make sure to update the ManagementFilterV6 with #the changes V6System1="2001:db8:a::123/64" V6System2="2001:db8:b::123/64" ManagementFilterV6=$V6System1,$V6System2 #Flush and zero all tables modprobe ip_tables modprobe ipt_limit modprobe iptable_mangle modprobe ipt_state modprobe ipt_LOG modprobe iptable_filter modprobe ipv6 iptables -F INPUT iptables -F FORWARD iptables -t nat -F POSTROUTING iptables -t nat -F PREROUTING ip6tables -F INPUT ip6tables -F FORWARD #init the log-and-drop chain iptables -F log-and-drop iptables -X log-and-drop iptables -N log-and-drop ip6tables -F log-and-drop ip6tables -X log-and-drop ip6tables -N log-and-drop iptables -F log-and-reject iptables -X log-and-reject iptables -N log-and-reject ip6tables -F log-and-reject ip6tables -X log-and-reject ip6tables -N log-and-reject #Remove/comment this out and all references to the FILTERS chain if Docker isn't being used #Restart Docker echo "Restarting Docker" systemctl restart docker #Now add in rules to affect DOCKER containers #See https://unrouted.io/2017/08/15/docker-firewall/ iptables -F DOCKER-USER iptables -X DOCKER-USER iptables -N DOCKER-USER iptables -F FILTERS iptables -X FILTERS iptables -N FILTERS echo "all tables flushed and dropped" # Specific chain used for logging packets before blocking them iptables -A log-and-drop -j LOG --log-prefix "[IPTables] Drop " iptables -A log-and-drop -j DROP ip6tables -A log-and-drop -j LOG --log-prefix "[IPTables] Drop " ip6tables -A log-and-drop -j DROP # Specific chain used for logging packets before blocking them iptables -A log-and-reject -j LOG --log-prefix "[IPTables] Reject " iptables -A log-and-reject -j REJECT ip6tables -A log-and-reject -j LOG --log-prefix "[IPTables] Reject " ip6tables -A log-and-reject -j REJECT echo "logging chains setup" #setup DOCKER-USER related rules- you will place all rules for Docker under the FILTERS chain iptables -A DOCKER-USER -i $INET_IF -j FILTERS # Check if NEW incoming tcp connections are SYN, drop if not iptables -A INPUT -p tcp ! --syn -m state --state NEW -j DROP iptables -A FILTERS -p tcp ! --syn -m state --state NEW -j DROP #Drop fragmented packets iptables -A INPUT -f -j DROP iptables -A FILTERS -f -j DROP iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --tcp-flags ALL FIN,URG,PSH -j DROP iptables -A FILTERS -p tcp --tcp-flags ALL FIN,URG,PSH -j DROP iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --tcp-flags ALL ALL -j DROP iptables -A FILTERS -p tcp --tcp-flags ALL ALL -j DROP # Drop incoming malformed XMAS packets iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --tcp-flags SYN,FIN SYN,FIN -m limit --limit 5/m --limit-burst 7 -j LOG --log-prefix "[IPT-XMAX Pkts] " iptables -A FILTERS -p tcp --tcp-flags SYN,FIN SYN,FIN -m limit --limit 5/m --limit-burst 7 -j LOG --log-prefix "[IPT-XMAX Pkts] " iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --tcp-flags SYN,FIN SYN,FIN -j DROP iptables -A FILTERS -p tcp --tcp-flags SYN,FIN SYN,FIN -j DROP #Drop all NULL pakcets iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --tcp-flags ALL NONE -m limit --limit 5/m --limit-burst 7 -j LOG --log-prefix "[IPT-NULL Pkts] " iptables -A FILTERS -p tcp --tcp-flags ALL NONE -m limit --limit 5/m --limit-burst 7 -j LOG --log-prefix "[IPT-NULL Pkts] " iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --tcp-flags ALL NONE -j DROP iptables -A FILTERS -p tcp --tcp-flags ALL NONE -j DROP iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --tcp-flags SYN,RST SYN,RST -j DROP iptables -A FILTERS -p tcp --tcp-flags SYN,RST SYN,RST -j DROP #Drop FIN packet scans iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --tcp-flags FIN,ACK FIN -m limit --limit 5/m --limit-burst 7 -j LOG --log-prefix "[IPT-FIN Scan] " iptables -A FILTERS -p tcp --tcp-flags FIN,ACK FIN -m limit --limit 5/m --limit-burst 7 -j LOG --log-prefix "[IPT-FIN Scan] " iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --tcp-flags FIN,ACK FIN -j DROP iptables -A FILTERS -p tcp --tcp-flags FIN,ACK FIN -j DROP iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --tcp-flags ALL SYN,RST,ACK,FIN,URG -j DROP iptables -A FILTERS -p tcp --tcp-flags ALL SYN,RST,ACK,FIN,URG -j DROP #Log and drop broadcast /multicast and invalid iptables -A INPUT -m pkttype --pkt-type broadcast -j LOG --log-prefix "[IPT-Broadcast] " iptables -A INPUT -m pkttype --pkt-type broadcast -j DROP iptables -A INPUT -m pkttype --pkt-type multicast -j LOG --log-prefix "i[IPT-Multicast] " iptables -A INPUT -m pkttype --pkt-type multicast -j DROP iptables -A INPUT -m state --state INVALID -j LOG --log-prefix "[IPT-Invalid] " iptables -A FILTERS -m state --state INVALID -j LOG --log-prefix "[IPT-Invalid] " iptables -A INPUT -m state --state INVALID -j DROP iptables -A FILTERS -m state --state INVALID -j DROP # The packets having the TCP flags activated are dropped # and so for the ones with no flag at all (often used with Nmap scans) iptables -A FORWARD -p tcp --tcp-flags ALL ALL -j log-and-drop iptables -A FILTERS -p tcp --tcp-flags ALL ALL -j log-and-drop iptables -A FORWARD -p tcp --tcp-flags ALL NONE -j log-and-drop iptables -A FILTERS -p tcp --tcp-flags ALL NONE -j log-and-drop ip6tables -A FORWARD -p tcp --tcp-flags ALL ALL -j log-and-drop ip6tables -A FORWARD -p tcp --tcp-flags ALL NONE -j log-and-drop #limit traffic to 80 an 443 - Change chain from INPUT to FILTERS to Docker and don't forget to open below #DCQ="2" #max requests in 1 second #DCH="25" #max requests over 7 seconds #iptables -A INPUT-p tcp --dport 80 -m state --state NEW -m recent --set --name P80QF --rsource #iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -m state --state NEW -m recent --update --second 1 --hitcount ${DCQ} --name P80QF --rsource -j log-and-drop #iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -m state --state NEW -m recent --set --name P80HF --rsource #iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -m state --state NEW -m recent --update --second 7 --hitcount ${DCH} --name P80HF --rsource -j log-and-drop #iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 443 -m state --state NEW -m recent --set --name P443QF --rsource #iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 443 -m state --state NEW -m recent --update --second 1 --hitcount ${DCQ} --name P443QF --rsource -j log-and-drop #iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 443 -m state --state NEW -m recent --set --name P443HF --rsource #iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 443 -m state --state NEW -m recent --update --second 7 --hitcount ${DCH} --name P443HF --rsource -j log-and-drop #default return chain for Docker- skipped. Enable if needed #iptables -A FILTERS -j RETURN #Global blocks #iptables -t filter -A INPUT -j DROP -s 12.34.56.78/32 #Limit DNS requests to prevent flood attacks - use if you are running a DNS server on the system this is installed on. #Don't forget to allow in the rules below # Requests per second #RQS="15" # Requests per 7 seconds #RQH="35" #iptables -A INPUT -p udp --dport 53 -m state --state NEW -m recent --set --name DNSQF --rsource #iptables -A INPUT -p udp --dport 53 -m state --state NEW -m recent --update --seconds 1 --hitcount ${RQS} --name DNSQF --rsource -j DROP #iptables -A INPUT -p udp --dport 53 -m state --state NEW -m recent --set --name DNSHF --rsource #iptables -A INPUT -p udp --dport 53 -m state --state NEW -m recent --update --seconds 7 --hitcount ${RQH} --name DNSHF --rsource -j DROP #Uncomment the next sections if using IPSEC #Clamp MSS on IPSEC tunnels #iptables -t mangle -A FORWARD -m policy --pol ipsec --dir in -p tcp -m tcp --tcp-flags SYN,RST SYN -m tcpmss --mss 1361:1536 -j TCPMSS --set-mss 1360 #iptables -t mangle -A FORWARD -m policy --pol ipsec --dir out -p tcp -m tcp --tcp-flags SYN,RST SYN -m tcpmss --mss 1361:1536 -j TCPMSS --set-mss 1360 # allow IPSEC from other boxes #IPSECsrc='XX.XX.XX.XX/YY' # Put in the form of XX.XX.XX.XX = IP address you want to allow IPSEC in from and YY is the netmask. #Technically the next two are not needed as we have the policy #iptables -A INPUT -i $INET_IF -p 50 -j ACCEPT --src "$IPSECsrc" #iptables -A INPUT -i $INET_IF -p 51 -j ACCEPT --src "$IPSECsrc" #iptables -A INPUT -i $INET_IF -p udp --dport 500 -j ACCEPT --src "$IPSECsrc" #iptables -A INPUT -i $INET_IF -p udp --dport 4500 -j ACCEPT --src "$IPSECsrc" # this is needed to allow all ipsec packets when it's host to host #iptables -A INPUT -m policy --dir in --pol ipsec -j ACCEPT --src "$IPSECsrc" #allow port 80 in #iptables -t filter -A INPUT -j ACCEPT --protocol tcp --dport 80 #iptables -t filter -A FILTERS -j ACCEPT --protocol tcp --dport 80 #ip6tables -t filter -A INPUT -j ACCEPT --protocol tcp --dport 80 #allow port 443 in #iptables -t filter -A INPUT -j ACCEPT --protocol tcp --dport 443 #iptables -t filter -A FILTERS -j ACCEPT --protocol tcp --dport 443 #ip6tables -t filter -A INPUT -j ACCEPT --protocol tcp --dport 443 # allow all ssh in - uncomment ManagementFilterV4 and comment out the lines below it to restrict SSH access on port 22 #iptables -t filter -A INPUT -j ACCEPT --protocol tcp --dport 22 --src $ManagementFilterV4 iptables -t filter -A INPUT -j ACCEPT --protocol tcp --dport 22 #uncomment ManagementFilterV6 and commentout the line below it to restruct SSH for IPv6 on port 22 #ip6tables -t filter -A INPUT -j ACCEPT --protocol tcp --dport 22 --src ManagementFilterV6 ip6tables -t filter -A INPUT -j ACCEPT --protocol tcp --dport 22 echo "end of services" # allow ping at 2 per sec iptables -t filter -A INPUT -j ACCEPT --in-interface $INET_IF --protocol icmp --icmp-type echo-request --match limit --limit 4/s --limit-burst 3 iptables -t filter -A INPUT -j log-and-drop --in-interface $INET_IF --protocol icmp --icmp-type echo-request ip6tables -A INPUT -p icmpv6 --icmpv6-type destination-unreachable -j ACCEPT ip6tables -A INPUT -p icmpv6 --icmpv6-type packet-too-big -j ACCEPT ip6tables -A INPUT -p icmpv6 --icmpv6-type time-exceeded -j ACCEPT ip6tables -A INPUT -p icmpv6 --icmpv6-type parameter-problem -j ACCEPT ip6tables -A INPUT -p icmpv6 --icmpv6-type echo-request -j ACCEPT ip6tables -A INPUT -p icmpv6 --icmpv6-type echo-reply -j ACCEPT ip6tables -A INPUT -p icmpv6 --icmpv6-type router-solicitation -m hl --hl-eq 255 -j ACCEPT ip6tables -A INPUT -p icmpv6 --icmpv6-type router-advertisement -m hl --hl-eq 255 -j ACCEPT ip6tables -A INPUT -p icmpv6 --icmpv6-type neighbor-solicitation -m hl --hl-eq 255 -j ACCEPT ip6tables -A INPUT -p icmpv6 --icmpv6-type neighbor-advertisement -m hl --hl-eq 255 -j ACCEPT ip6tables -A INPUT -p icmpv6 --icmpv6-type 141 -m hl --hl-eq 255 -j ACCEPT ip6tables -A INPUT -p icmpv6 --icmpv6-type 142 -m hl --hl-eq 255 -j ACCEPT ip6tables -A INPUT -p icmpv6 --icmpv6-type 130 -s fe80::/10 -j ACCEPT ip6tables -A INPUT -p icmpv6 --icmpv6-type 131 -s fe80::/10 -j ACCEPT ip6tables -A INPUT -p icmpv6 --icmpv6-type 132 -s fe80::/10 -j ACCEPT ip6tables -A INPUT -p icmpv6 --icmpv6-type 143 -s fe80::/10 -j ACCEPT ip6tables -A INPUT -p icmpv6 --icmpv6-type 148 -m hl --hl-eq 255 -j ACCEPT ip6tables -A INPUT -p icmpv6 --icmpv6-type 149 -m hl --hl-eq 255 -j ACCEPT ip6tables -A INPUT -p icmpv6 --icmpv6-type 151 -s fe80::/10 -m hl --hl-eq 1 -j ACCEPT ip6tables -A INPUT -p icmpv6 --icmpv6-type 152 -s fe80::/10 -m hl --hl-eq 1 -j ACCEPT ip6tables -A INPUT -p icmpv6 --icmpv6-type 153 -s fe80::/10 -m hl --hl-eq 1 -j ACCEPT # allow responces to local initated connections #iptables -A INPUT -i $INET_IF --match state --state NEW,INVALID -j log-and-drop #iptables -A FORWARD -i $INET_IF --match state --state NEW,INVALID -j log-and-drop iptables -t filter -A INPUT -j ACCEPT --match state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED ip6tables -t filter -A INPUT -j ACCEPT --match state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED # Set rp_filter to 2 for i in `find /proc/sys/net/ipv*/conf -name rp_filter` do echo "2" >$i done # setup a default deny rule for outside traffic iptables -t filter -A INPUT --in-interface $INET_IF -j log-and-drop iptables -t filter -A FILTERS --in-interface $INET_IF -j log-and-drop ip6tables -t filter -A INPUT --in-interface $INET_IF -j log-and-drop #uncomment the next two lines if fail2ban is installed #echo "Restarting fail2ban" #systemctl restart fail2ban
External Links
- ↑ strongSwan Official Site [1]
- ↑ MikroTik Official Site [2]
- ↑ OpenVPN Official Site [3]
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Road warrior (computing) [4]
- ↑ Tinc-vpn Official Site [5]
- ↑ SoftEther VPN Official Site [6]
- ↑ WireGuard Offical Site [7]
- ↑ Mikrotik Forums - MikroTik Wireguard server with Road Warrior clients [8]
- ↑ VPNC Project Homepage [9]